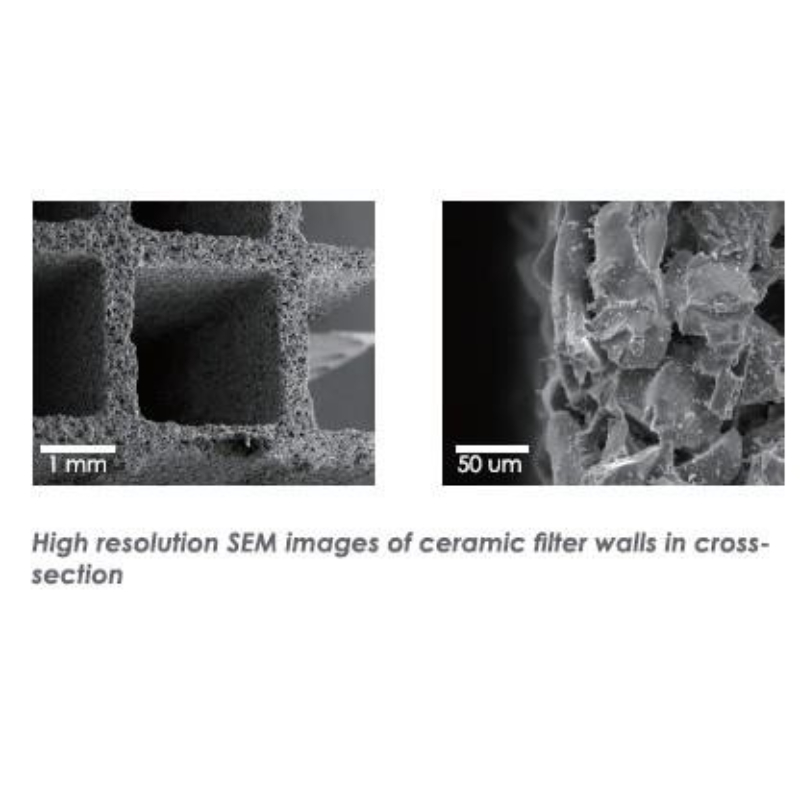
-
商品資訊
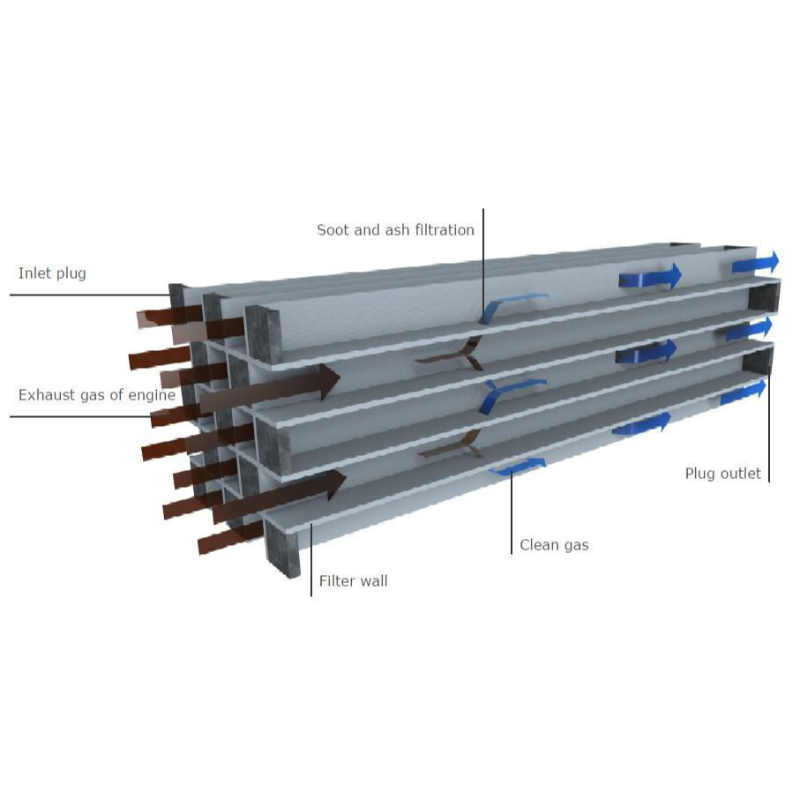
### Description of DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter)
A Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is a device designed to remove particulate matter (PM), specifically soot and ash, from the exhaust gas of a diesel engine. It is an essential component in modern diesel engines, particularly for reducing harmful emissions and complying with stringent environmental regulations.
### 1. Working Principle
The DPF is installed in the exhaust system of diesel engines and works by trapping particulate matter. The exhaust gases flow through a porous ceramic material in the filter, where the particulate matter is captured on the walls of the filter's channels. Over time, the accumulated soot is periodically burned off in a process called **regeneration**, which occurs either passively or actively:
- **Passive Regeneration**: This happens automatically when the exhaust temperature is high enough to burn the soot particles during normal engine operation.
- **Active Regeneration**: This occurs when the engine control unit (ECU) initiates additional measures, such as injecting extra fuel or using a dedicated heating element, to raise the exhaust temperature and burn off the soot.
### 2. Key Features
- **Particulate Matter Reduction**: DPFs are highly effective in reducing particulate emissions by up to 85-95%, making them crucial for meeting Euro 6 and other emission standards.
- **Regeneration Process**: Depending on the engine and driving conditions, regeneration cycles may occur frequently, especially if the vehicle is used for short trips or under low load conditions, where passive regeneration may not be sufficient.
- **Material Composition**: DPFs are usually made from ceramic materials such as cordierite or silicon carbide. These materials are highly resistant to thermal shock and have excellent filtering capabilities.
### 3. Applications
DPFs are widely used in diesel-powered vehicles, including:
- **Passenger Cars**: All modern diesel cars are equipped with DPFs to comply with emissions regulations.
- **Commercial Vehicles**: Trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles also rely on DPF technology to reduce particulate emissions.
- **Non-Road Mobile Machinery**: DPFs are also found in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and other non-road diesel engines.
### 4. Maintenance and Considerations
- **Regeneration Monitoring**: It is essential to monitor the DPF regeneration process to ensure it is functioning correctly. Vehicles equipped with DPFs usually have sensors to measure backpressure and alert the driver if regeneration is required or if the DPF is becoming clogged.
- **Clogging Issues**: If the DPF fails to regenerate properly, it can become clogged with soot, leading to increased backpressure, reduced engine performance, and potentially severe engine damage. Regular driving at higher speeds can help ensure the DPF stays clean through passive regeneration.
- **DPF Replacement**: Over time, ash accumulation (from engine oil and additives) can clog the DPF beyond what regeneration can clean, necessitating a replacement, usually after around 100,000 to 200,000 kilometers, depending on the vehicle and operating conditions.
### 5. Advantages
- **Environmental Impact**: DPFs play a critical role in reducing the environmental impact of diesel engines by significantly lowering particulate matter emissions, which are harmful to human health and the environment.
- **Regulatory Compliance**: Vehicles equipped with DPFs are able to meet stringent emissions standards, ensuring they can operate in regions with strict environmental laws.
### 6. Disadvantages
- **Cost**: The inclusion of a DPF system increases the overall cost of diesel vehicles due to the complexity of the filter and regeneration mechanisms.
- **Fuel Consumption**: Active regeneration can increase fuel consumption slightly due to the need for extra fuel injection during the regeneration process.
- **Maintenance**: Drivers must be aware of the DPF regeneration process and occasionally may need to adjust their driving patterns to ensure proper DPF operation.
### Summary
The Diesel Particulate Filter is a vital component in modern diesel engines for reducing particulate emissions. While it requires careful maintenance and can increase costs, it is essential for meeting environmental regulations and reducing the harmful effects of diesel exhaust on air quality and public health.
針對過濾器的比較與描述
Filter type
過濾器類型
Filtration efficiency
過濾效率
Catalytic coating
催化塗層
Operation under MDO conditions
燃用MDO條件下
Standard automotive SiCfilter
標準車用SiC過濾器
> 97%
Mainly noble metals based, Sulphur poisoning
主要基於貴金屬,有硫中毒風險
few weeks
幾周
Hug SiCfilter with improved morphology
HUG改進的SiC過濾器
>97% (VERT certificate)
>97% (VERT認證)
Vanadium based, Sulphur insensible
釩基,無硫中毒風險
≥ 3`000 working hours
≥ 3`000 運行小時
Hug FA2 filter with improved morphology
HUG改進的FA2過濾器
>97% Black carbon
>97% 黑煙
Vanadium based, Sulphur insensible
釩基,無硫中毒風險
≥ 3`000 working hours and 75% of SiC-volume
≥ 3`000 運行小時且僅有75%的體積
針對載體的描述
- •Material of Substrate: Oxide bound silicon carbide (Hug-Patent)
載體材料:碳化矽氧化物(HUG專利)
- •Cell density up to 200 cpsi
孔密度高達200cpsi
- •Nominal surface of substrate up to 1700 m2/m3
•比表面積可達1700 m2/m3
- •Short term peak temperature for substrate up to 1300 degree C
基體的短期耐受峰值溫度高達1300℃
- •New FA2 substrate to improve the performance
新開發基體FA2性能提升
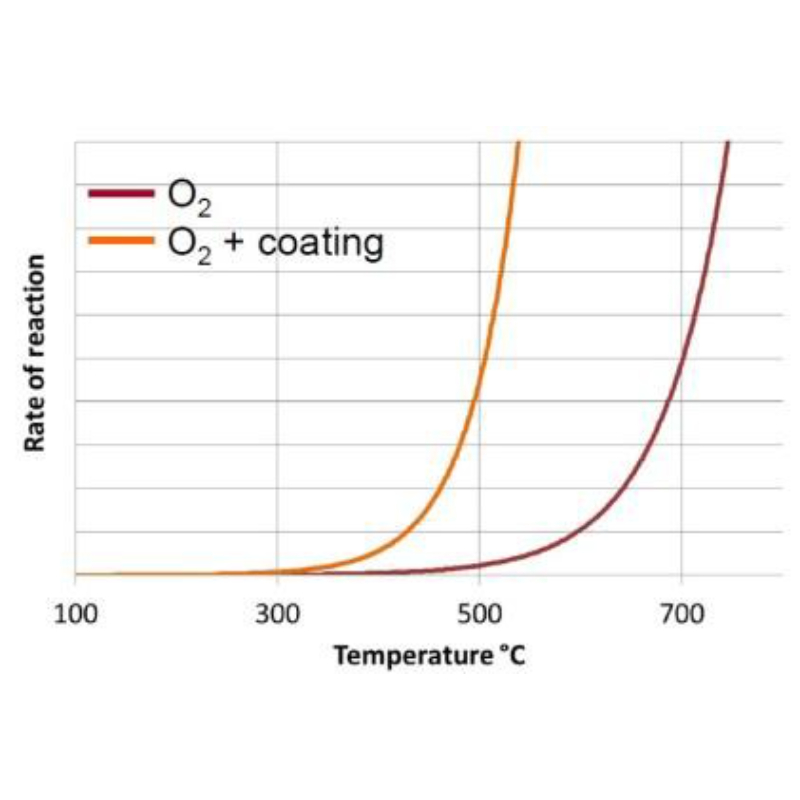
針對塗層的描述
- HUG DPF are coated with catalytic active material to lower the temperature for regeneration HUG DPF
塗有催化活性材料,可以降低再生溫度
- •Material of Coating: Vanadium based/Alkali based
塗層材料:釩基/堿基
- •Short term peak temperature for coating up to 700 degree C
塗層的短期耐受峰值溫度高達700℃
- •Max. operating temperature for coating up to 600 degree C
塗層最高的運行溫度600℃
-
商品Q&A